The Mechanism of UV-Resistant Finishing
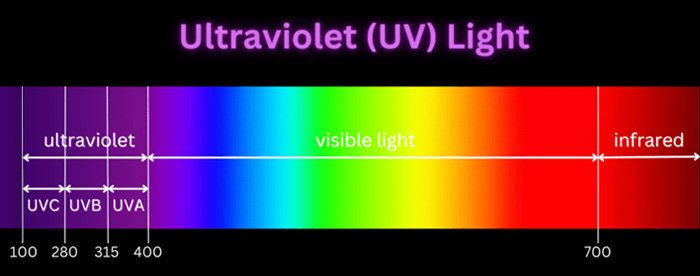
From an optical perspective, when light is projected onto an object, a portion of it reflects off the surface, some is absorbed by the object, and the rest passes through the object. In general, the sum of transmittance rate, reflectance rate, and absorbance rate equals 100%.
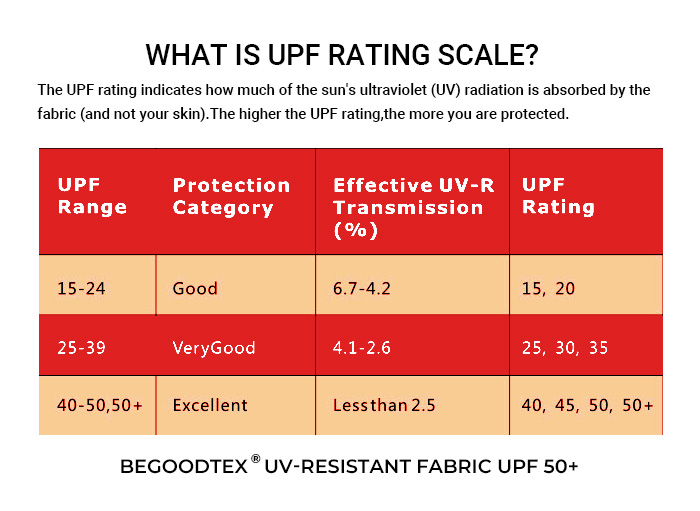
The principle of UV-resistant processing involves using UV blockers to treat fibers or fabrics.
When light radiation reaches the fabric, a small portion passes through the gaps in the fabric, while most of it is reflected or selectively absorbed by the UV blockers. The absorbed light is converted into low energy, which is then released, effectively blocking the UV radiation.
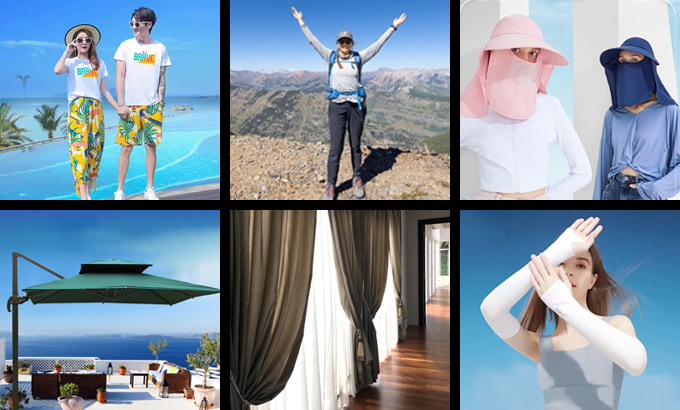
UV-Resistant Textiles Production
The production of UV-resistant textiles belongs to the category of textile post-treatment. It primarily involves the application of UV-resistant finishing agents, the preparation of finishing solutions, and the selection of appropriate finishing processes.
The finishing process of UV-resistant fabrics depends on the type of fabric and its intended use. For example, summer clothing requires high softness and comfort, and it is better to use absorption or impregnation methods for UV-resistant finishing.
When used as decorative, household, or industrial textiles, the focus is on their functional requirements, and surface coating methods can be applied.
For UV-resistant finishing of blended fabrics, impregnation and rolling-baking methods are still preferred from a technical standpoint. This process has less impact on fiber properties, fabric style, moisture absorption, and strength. Additionally, it can be combined with other functional finishes like antibacterial, deodorant, hydrophilic, and wrinkle-resistant finishes.